In our previous article of Indian Space Program-Part-1, we have talked about an introductory part of Indian Space Journey, Let's Talk about milestones of Success, Gained by ISRO in detail, click here to read Part-1 of this article.
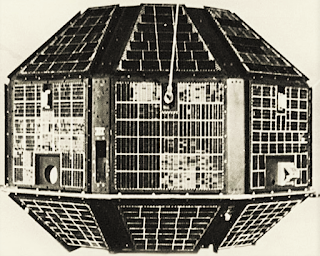 It was launched in space on April 19, 1975 by the Soviet Rocket Inter Cosmos. This was the first satellite of the country. This satellite was made from indigenous technology and was launched at 12:52 pm according to Indian time. It was 307 kg in weight. It entered Earth's orbit above Indonesia at 1:28 a.m., which was later established in its predetermined orbit at an elevation of 594 kilometers.
It was launched in space on April 19, 1975 by the Soviet Rocket Inter Cosmos. This was the first satellite of the country. This satellite was made from indigenous technology and was launched at 12:52 pm according to Indian time. It was 307 kg in weight. It entered Earth's orbit above Indonesia at 1:28 a.m., which was later established in its predetermined orbit at an elevation of 594 kilometers.With the successful launch of this satellite, India has become the second nation after the China in the developing countries and eleventh nation in the world in the field of space research. Nations that launch satellite in space before India are the United States, the Soviet Union, Germany, China, France, England, Australia, Canada, Japan, and Italy.
Aryabhata was the first satellite developed by ISRO, developed as a scientific satellite. It was a nearly circular compound made of 26 flat elements, it's diameter was 1.6 meters and 1.2 meters in height. This satellite was to be used for X-ray, astronomy, air science experiment and solar physics experiment in its brief working hours of March 6. Aryabhata did them efficiently, although the procedure of this satellite was only pegged to 6 months it remained in space until March 1980.
Bhaskara Series
With the successful launch of its first satellite Aryabhata, the Indian scientific Geo-projection satellite was oriented towards the creation of "Bhaskara" and in this series, two planets named Bhaskara-I and Bhaskara-II were produced and successfully launched.
Bhaskara-I
 This was an experimental Ground-launch satellite, launched from the Soviet Cosmodrome on June 7, 1979. The weight of this satellite was 444 kilograms, height was 1.18 meters and diameter was 1.55 meters. This satellite was installed in its predetermined orbit at a height of 525 kilometers from the Earth and measured entire India three times of its 104 terrestrial planets, in its lifetime (2 years).
This was an experimental Ground-launch satellite, launched from the Soviet Cosmodrome on June 7, 1979. The weight of this satellite was 444 kilograms, height was 1.18 meters and diameter was 1.55 meters. This satellite was installed in its predetermined orbit at a height of 525 kilometers from the Earth and measured entire India three times of its 104 terrestrial planets, in its lifetime (2 years).The speed of data transmission of this satellite was much more than that of "Aryabhata", because 250 orders could be given by its modern and complex order system, while Aryabhata was able to take only 35 orders. Bhaskara-I was also 84 kilograms more than Aryabhata in terms of weight.
With this satellite two major remote sensing policymakers (television camera system and microwave window system) were taken.
Important data were obtained from two television cameras and three microscopic radiogamy instruments installed in this satellite, including meteorological information such as sea surface temperature, sea breeze, atmospheric humidity, mapping of flood affected and flood free areas, in addition to meteorological information. This satellite has been successful in achieving its Geo-related targets of glaciation, snow fall, forestry, hydrology, geophysical compositions and ocean science.
Bhaskara-II
 In Bhaskara Series, a second and last satellite named "Bhaskara-II" was launched on November 20, 1981 with Soviet Cosmodrome and by launching it, an attempt to remove all the flaws existing in Bhaskara-I was made. Due to Bhaskara-I's placement, its technical nature, i.e. size, policy structure and systems were kept almost same and it was also installed in orbit at a height of 525 km from the earth.
In Bhaskara Series, a second and last satellite named "Bhaskara-II" was launched on November 20, 1981 with Soviet Cosmodrome and by launching it, an attempt to remove all the flaws existing in Bhaskara-I was made. Due to Bhaskara-I's placement, its technical nature, i.e. size, policy structure and systems were kept almost same and it was also installed in orbit at a height of 525 km from the earth.The distance of this satellite, (controlled by Sriharikota and Ahmedabad based control rooms) was kept perpendicular to its class room, which facilitates proper deployment of its television cameras. There were also two television cameras installed in it, which were able to take a clear picture of land area of 340 sq km.
 It included three Satellite Microwave Radiometer-SAMIR which was capable of measuring 340 square kilometers. Apart from this, it was also able to identify items of distance of 100 meters due to their extreme sensitivity. They had the ability to work in all times and every season.
It included three Satellite Microwave Radiometer-SAMIR which was capable of measuring 340 square kilometers. Apart from this, it was also able to identify items of distance of 100 meters due to their extreme sensitivity. They had the ability to work in all times and every season.Through the SAMIR devices engaged in this satellite, success has been achieved in analyzing marine surfaces, maritime conditions, the amount of water vapor in any area, the arrival of floods and its landing, and the occurrence of melting and melting of ice etc.
APPLE
 APPLE was an experiment in the direction of telecommunications satellites whose full name is "Ariane Passenger PayLoad Experiment". This satellite was launched on June 19, 1981 by the Ariane Rocket of the European Space Agency. This was the result of the design and construction of the entire Indian resources. It's main structure was 1.20 meters in diameter, while the length was 1.20 meter in the tube. It's weight was 763 kg and it's launch created the foundation stone for launch of Indian National satellites like "INSAT".
APPLE was an experiment in the direction of telecommunications satellites whose full name is "Ariane Passenger PayLoad Experiment". This satellite was launched on June 19, 1981 by the Ariane Rocket of the European Space Agency. This was the result of the design and construction of the entire Indian resources. It's main structure was 1.20 meters in diameter, while the length was 1.20 meter in the tube. It's weight was 763 kg and it's launch created the foundation stone for launch of Indian National satellites like "INSAT".In fact, it was the only First Telecommunication Satellite experiment in the geostationary orbit of the country. The geostationary orbit was 36000 kilometers. It has succeeded in providing its experience in the use of national communication, radio broadcasting, data transmission, remote area communication etc. The most important thing about its launch was that the fourth stage motor of the country's SLV-3 rocket was also used as an API Booster Motor in it.
Check below links:
- Bhangarh Fort-India's most Haunted and Scary place
- Top 8 Mysterious Places on Earth
- Most Amazing Android Applications you should try












0 Comment Here:
Post a Comment
Share your Feedback